🔬 Observational study: Nahibu is looking for volunteers with sleep disorders to analyze their gut microbiota.

What is a healthy and balanced diet?
What is a healthy and balanced diet?
According to the World Health Organization, chronic diseases linked to diet, such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, are the leading cause of death worldwide. The influence of our diet on our health is becoming increasingly well known, and the risk of developing these diseases can now be reduced by adopting a healthy diet. A varied and balanced diet is essential for the body. It enables it to function optimally and reduces the risk of developing diseases.
How important is a healthy diet?
Eating is a vital need. The nutrients provided by food are essential for the body. They are divided into energy-producing and non-energy-producing nutrients. Energy nutrients, represented by macronutrients (fats, carbohydrates, proteins), provide the body with energy in the form of calories, while non-energy nutrients, or micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, amino acids, enzymes, etc.), enable the body's biological processes to function properly. If nutrient intake is insufficient, nutritional deficiencies occur, i.e., an imbalance between nutrient intake and requirements, which often has significant consequences for health.

What does the human body need?
To function properly, the body needs a sufficient and regular supply of energy and nutrients. Nutritional needs include water, energy, nutrients, vitamins, and minerals. They enable the body to develop, renew tissue, and maintain good overall physical and mental health. These needs are normally met by a varied and balanced diet.
An appropriate calorie intake
Daily calorie intake depends on several factors such as gender, age, body size, and physical activity. For women, the recommended calorie intake is approximately 2,000 to 2,200 kilocalories (kcal) per day, depending on age and physical activity. For men, it is 2,500 to 2,700 kcal. If you exercise, your calorie intake should be increased in proportion to the intensity of the activity. For example, during very intense physical activity, calorie intake can reach 2600 kcal for women and 3400 kcal for men. The amount of calories needed each day also depends on age. Calorie intake decreases with age. It is important to note that insufficient calorie intake can cause serious health problems. It can lead to micronutrient deficiencies and thus to numerous hormonal and bone disorders, etc.
Adequate nutrient intake
Proteins
Proteins are made up of chains of amino acids. There are 22 different amino acids, 8 of which are known as essential. This means that since the body cannot synthesize them, they must be obtained from food. The others are synthesized by the body using the proteins present. To ensure an adequate intake of amino acids, the proteins ingested must be sufficient and varied. Proteins are involved in many structural, metabolic, and immune functions.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates, more commonly known as sugars, are responsible for providing the body with energy in the form of calories. There are two types of carbohydrates: simple and complex.
Foods are differentiated according to their glycemic index, which indicates a food's ability to raise blood sugar levels (glycemia). The higher the index, the faster blood sugar levels rise. A high glycemic index requires the pancreas to release insulin to lower blood sugar levels; insulin converts glucose into glycogen, which is used as energy. If there is excess glycogen, glucose is converted into fat, which is why sugar can cause weight gain.
Dietary fiber is a complex carbohydrate of plant origin that is neither digested nor absorbed by the body. Fiber is naturally present in plant-based foods.
Some simple carbohydrates, such as fructose, occur naturally in fruits, while others, such as glucose and galactose, are added to foods before they reach our plates. Regardless of their origin, simple carbohydrates are responsible for sweetness and provide the body with immediate energy.
Complex carbohydrates are formed by a chain of simple sugars and are found in legumes, tubers, and cereals. Unlike simple carbohydrates, they provide the body with energy more gradually. In addition, they are absorbed by the body much more slowly.
Lipids
Lipids are more commonly known as fats and are essential for the body to function properly. They are divided into saturated fatty acids, unsaturated fatty acids, and trans fatty acids. Lipids require special attention because many of them should be limited. Saturated fatty acids provide energy and vitamins and are part of the composition of cell membranes. Unsaturated fatty acids are broken down into omega-3, 6, and 9. Omega-3 and 9 are to be favored, while omega-6, if consumed in excess, impacts the functioning of omega-3 and 9. Finally, trans fatty acids result from a process of hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids carried out in the food industry to increase their stability and shelf life. They are not natural. These differences therefore require us to pay attention to the type of fat we consume in order to favor the good and limit the bad. For example, it is recommended to reduce trans fatty acid consumption as much as possible, as they are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Minerals
Minerals include major minerals and trace elements, both of which are essential for the body as they are involved in many chemical reactions. Major minerals include magnesium, sodium, potassium, and calcium.
Vitamins
Vitamins are essential for the body to function properly because they are involved in many functions. They are obtained exclusively from food. The necessary daily intake varies from person to person. There are 13 vitamins that play a role in various functions: vitamins A, C, D, E, K, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B8, B9, and B12.
Shido, nutritional advice tailored to your gut microbiota.
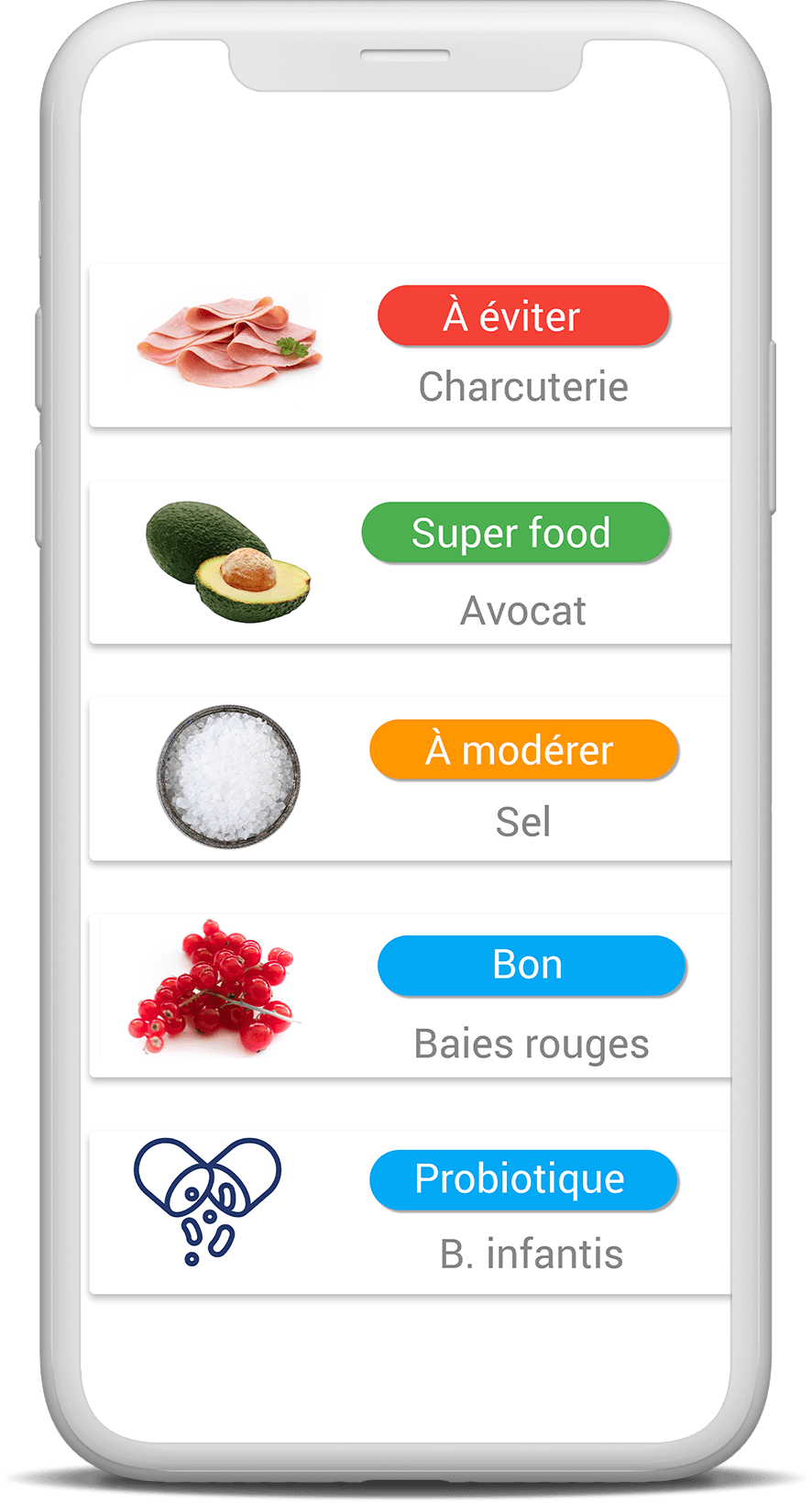
What constitutes a balanced diet?
Eating a varied and balanced diet means eating well and in quantities that allow the body to function properly.
First of all, since no single food can meet the body's daily nutritional needs on its own, it is recommended to combine several foods in a meal. This increases the number of nutrients that will be delivered to our cells during digestion. During digestion, food is broken down by enzymes into macronutrients and micronutrients and transported to the organs via the bloodstream.
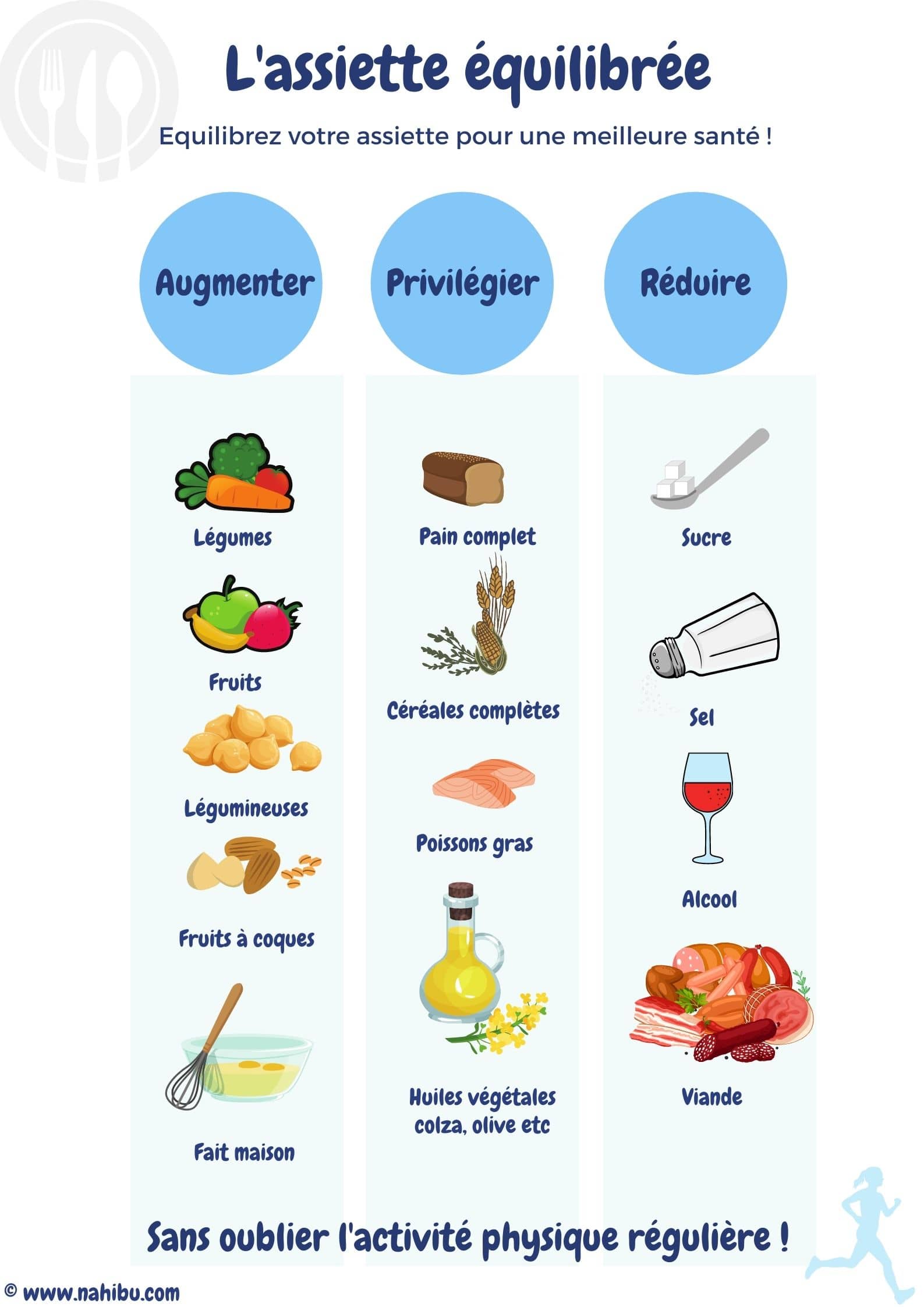
Eating well also means choosing foods that are good for your health over those that are less healthy. In particular, it is recommended to increase your consumption of fruits, vegetables, legumes (lentils, beans, chickpeas, split peas, broad beans, etc.), unsalted nuts (walnuts, almonds, etc.) and to opt for homemade foods as much as possible to limit the potential intake of additives that have no nutritional value.
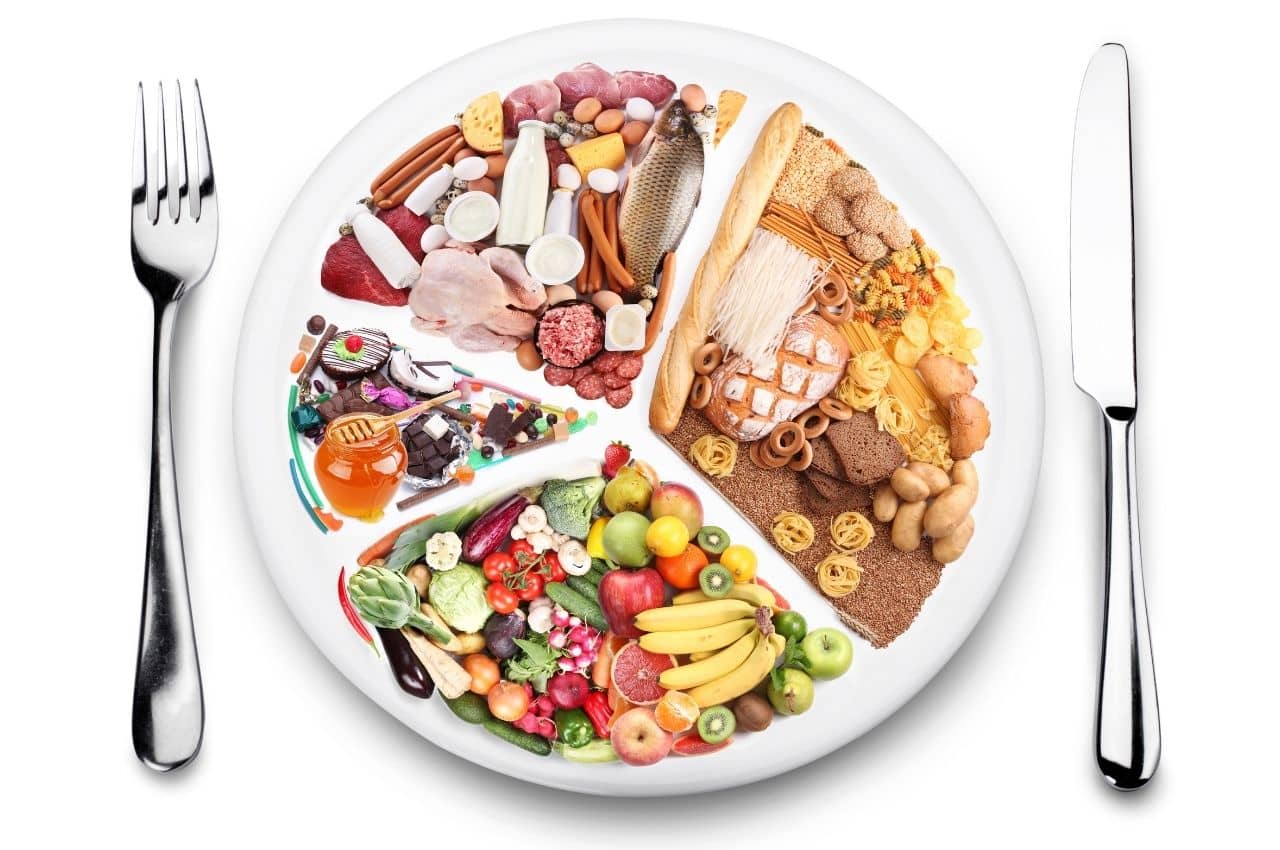

You should reduce your intake of alcohol, sugary foods and drinks, salty foods, meat (pork, beef, veal, lamb, mutton), charcuterie, and products with a Nutri-score between D and E. The Nutri-score assesses the nutritional quality of a product, from A, a very favorable product in terms of nutrition, to E, an unfavorable product, based on its nutrient composition, foods to favor (fiber, fruits, vegetables, proteins), and foods to limit (sugar, salt, calories, saturated fatty acids).
Finally, it is important to prioritize whole, unrefined foods: whole grain bread, cereals, and starchy foods, as well as healthy fats found in oily fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel, etc.) and vegetable oils, particularly rapeseed and olive oil. It is also important to note that a balanced diet is not determined by a single meal, but is built up over several meals. This is why it is entirely possible to restore balance with lighter, more balanced meals after a heavier, higher-calorie festive meal.
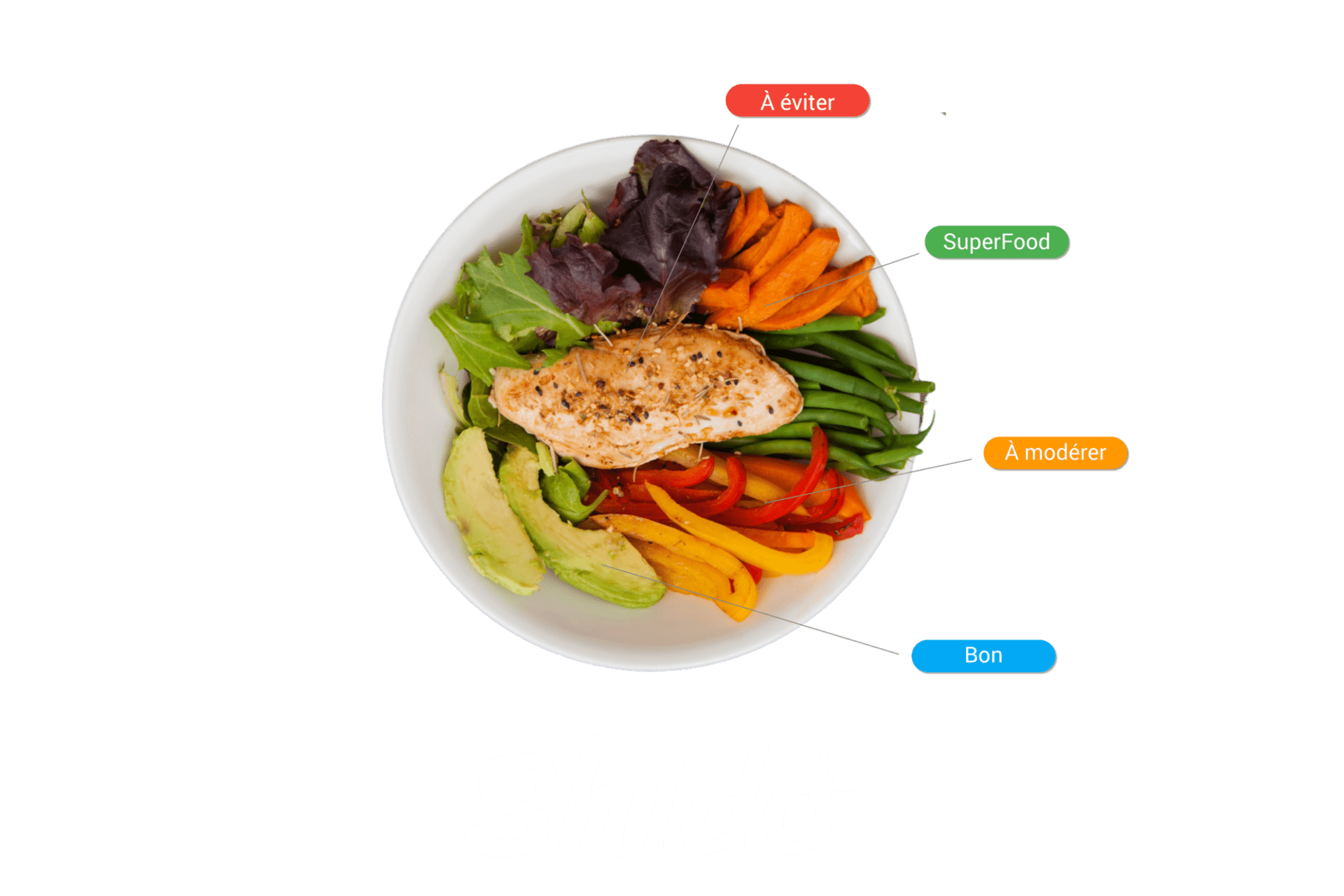
Put simply, to provide the body with everything it needs, your plate should be composed as follows: ½ vegetables, ¼ protein, and ¼ starchy foods.
When it comes to vegetables, it is best to choose fresh, seasonal produce, as these will be richer in nutrients and free from preservatives and other additives that can be found in canned vegetables. It is also recommended to vary your vegetable intake to fully benefit from the different health benefits they can provide.
Daily protein intake depends on body size. It is recommended to consume 1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight, or 60 grams for a person weighing 60 kilograms. As with vegetables, it is important to vary your sources of protein between plant and animal sources.
The last quarter of the plate is reserved for starchy foods. However, this may vary depending on the individual's physical activity and energy expenditure. Among starchy foods, it is advisable to consume those with a low or moderate glycemic index rather than those with a high glycemic index, as the latter promote fat storage.
In addition to this, there are portions of fruit, healthy fats, and possibly dairy products. Fruit is a source of antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which are essential for good health. As for fats, not all of them should be avoided. However, it is important to favor the consumption of healthy fats and limit unhealthy fats.

Not forgetting physical activity
In addition to eating a balanced diet, it is essential to engage in regular physical activity and limit sedentary behavior as much as possible, as it poses health risks. Physical activity is the ultimate health ally: it contributes to daily well-being and, even more importantly, helps maintain good overall health. It is also associated with a reduction in disease.
What's more, playing sports releases endorphins in the brain, in proportion to the intensity, duration, and nature of the physical activity. More commonly known as happiness hormones, endorphins bring about feelings of pleasure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is essential to have a varied and balanced diet to enable the body to function properly and also to engage in regular physical activity. However, as Paracelsus said, Everything is poison and nothing is without poison; only the dose makes something not a poison. Balanced and varied does not mean restrictive; you can eat everything, it's all about quantity. Nevertheless, it is important to favor healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, etc., and limit sugary and salty foods, processed meats, red meat, alcohol, fats, etc.
Sources:
Nutrition and health. INSERM. Available at: https://www.inserm.fr/information-en-sante/dossiers-information/nutrition-et-sante
Balanced diet. Eating well for well-being. French Cardiology Federation. Available at: https://www.fedecardio.org/sites/default/files/image_article/BROCHURE-Alimentation.pdf
Nutritional requirements and dietary intake for adults. Collegiate Society of Hepato-Gastroenterology Specialists. Available at this link.
Nutritional recommendations for ages 18 to 75. VIDAL. Available at: https://www.vidal.fr/sante/nutrition/equilibre-alimentaire-adulte/recommandations-nutritionnelles-adulte.html
What you need to know about carbohydrates. French Cardiology Federation. Available at: https://www.fedecardio.org/Je-m-informe/Je-mange-equilibre/ce-qu-il-faut-savoir-sur-les-glucides
Discover more articles on the microbiota.
Microbiota Study: Nahibu is looking for volunteers suffering from sleep disorders!
Partnership between Nutri&Co; and Nahibu
Certified Low-FODMAP by Monash University (a leader in FODMAP research), the Organic Fiber formula developed by Nutri&Co. is specifically designed using clinically documented dietary fibers to enable people with IBS to consume more fiber without experiencing discomfort.
Partnership between Quan Sports and Nahibu
Quan Sports is an agency that supports sports professionals in various areas: mental preparation (QuanLife), physical performance optimization (QuanBest), image management and communication (MyQuan), and preparation for the future (QuanFutur).
Take control of your diet with Shido.