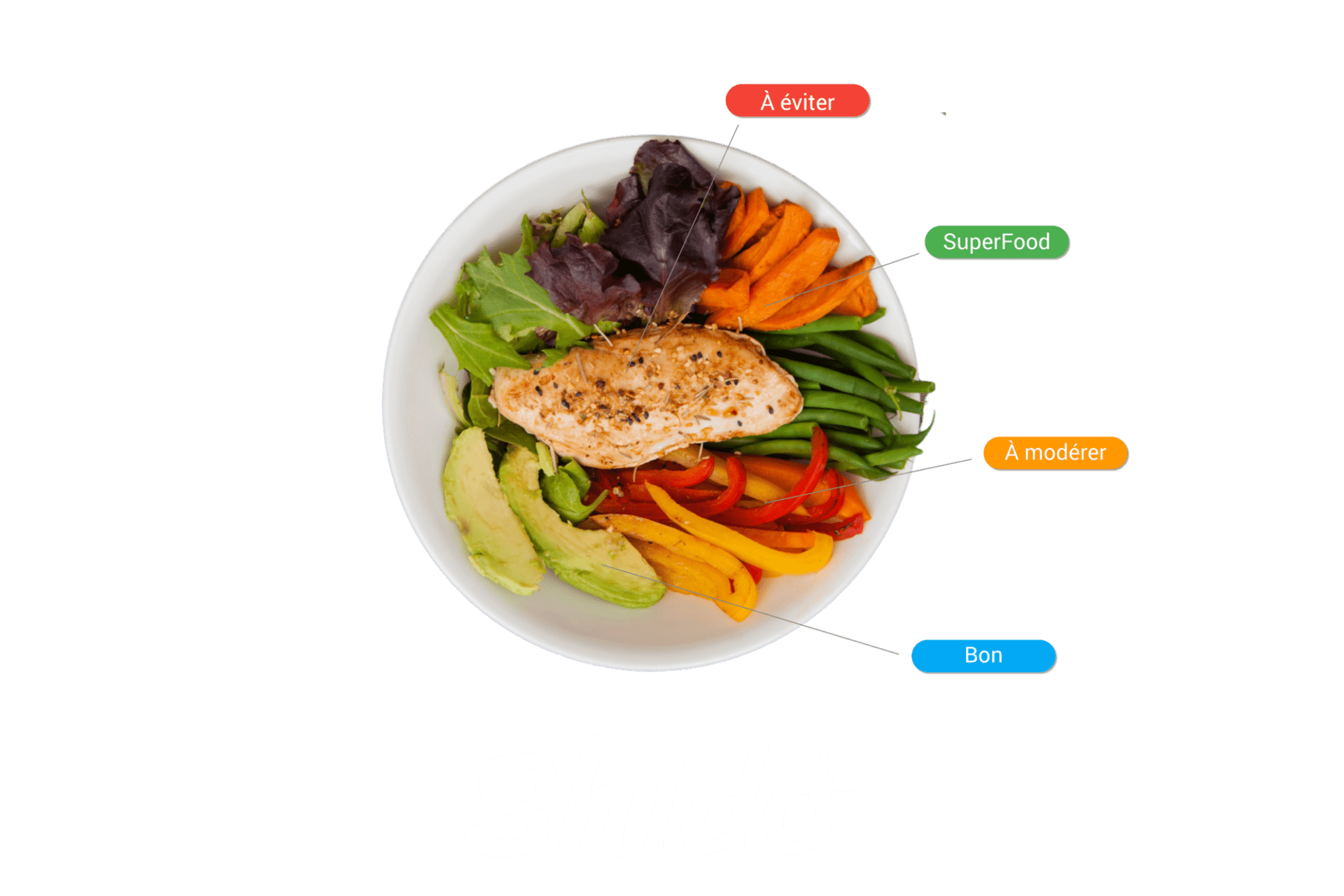
The increase in sugar in our diet is not without consequences for our health. It can cause obesity, metabolic disorders, dysbiosis, etc.

Top 5 meat alternatives
Top 5 meat alternatives
Meat alternatives are experiencing rapid growth. Tofu, tempeh, seitan, plant-based meat, steak… these foods are becoming increasingly common on supermarket shelves and are no longer consumed only by vegans or vegetarians. Today, many people are reducing their meat consumption for environmental, animal welfare, or health reasons.
What nutrients does meat provide?
In addition to providing protein, meat is also a significant source of trace elements, minerals, and vitamins. Meat is rich in heme iron, which is easily absorbed by the body. Finally, it is a source of vitamin B12.

What are our needs?
Proteins, which are made up of amino acids, including eight essential ones, are essential for the body because they enable it to perform structural, metabolic, and immune functions. ANSES recommends a daily protein intake of 0.83 grams per kilogram, or 49.8 grams for a person weighing 60 kilograms. Iron is mainly used in the production of hemoglobin, which enables oxygen to be transported in the blood.
It is recommended that you consume around 11 milligrams (16 mg for women with heavy periods) per day to meet the body's needs. Finally, vitamin B12, as a coenzyme (a molecule that catalyzes an enzymatic reaction), performs functions in the blood and neurons. According to ANSES, the daily requirement for vitamin B12 is approximately 2.4 micrograms for adults.

What foods can replace meat?
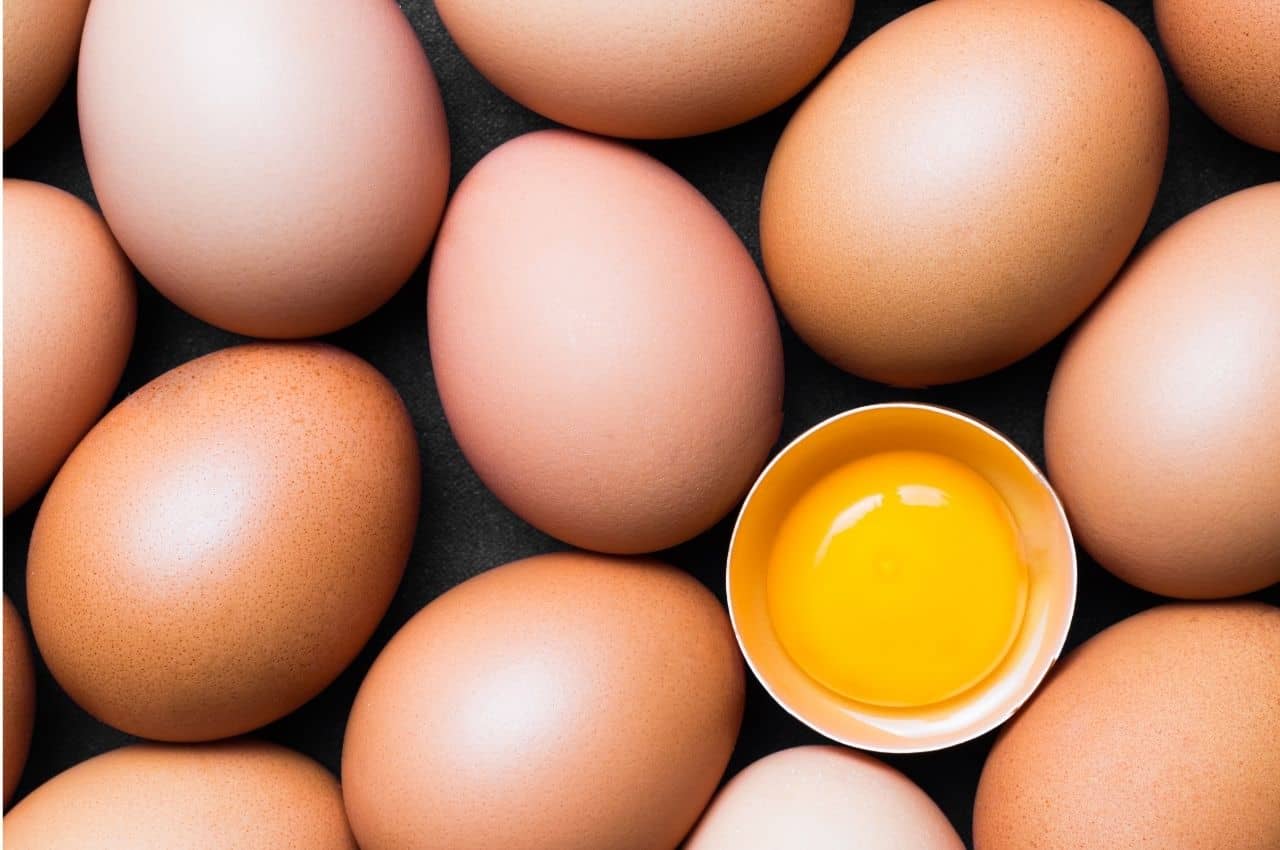
Eggs
Eggs contain 13.5 grams of protein per 100 grams and provide the body with the essential amino acids it needs to function. They are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, minerals (iron, selenium, zinc, phosphorus), and vitamins (A, B1, B3, B12, E, D). The cholesterol they contain has no effect on blood cholesterol levels because very little is absorbed by the intestine. Finally, they are low in calories, with 100 grams of eggs containing only 134 kilocalories.
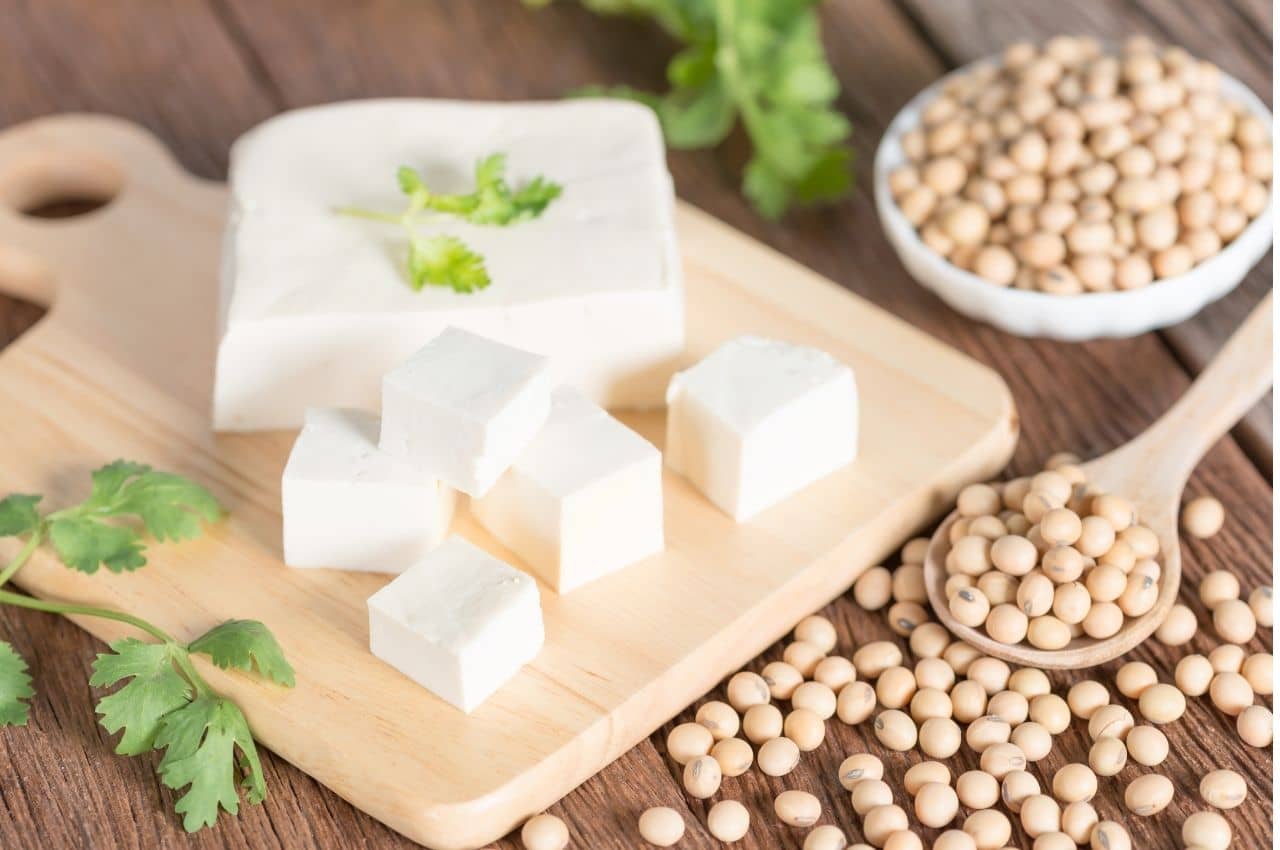
Tofu
Tofu is made from soybeans. Rich in protein (13.4 per 100 grams), it is regularly consumed in meat-free diets and has also been eaten in Asian countries for a very long time. It is also a source of omega-3, minerals (calcium, iron, zinc), and B vitamins. In addition, tofu is low in calories (148 kilocalories per 100 grams) and free of unhealthy fats.

Seitan
Seitan is made from rehydrated wheat gluten. Rich in protein (20.6 grams per 100 grams), iron, and free of saturated fat, it is an interesting alternative to meat. In addition to being low in calories (134 kilocalories per 100 grams), its high fiber content facilitates intestinal transit and promotes a feeling of fullness.
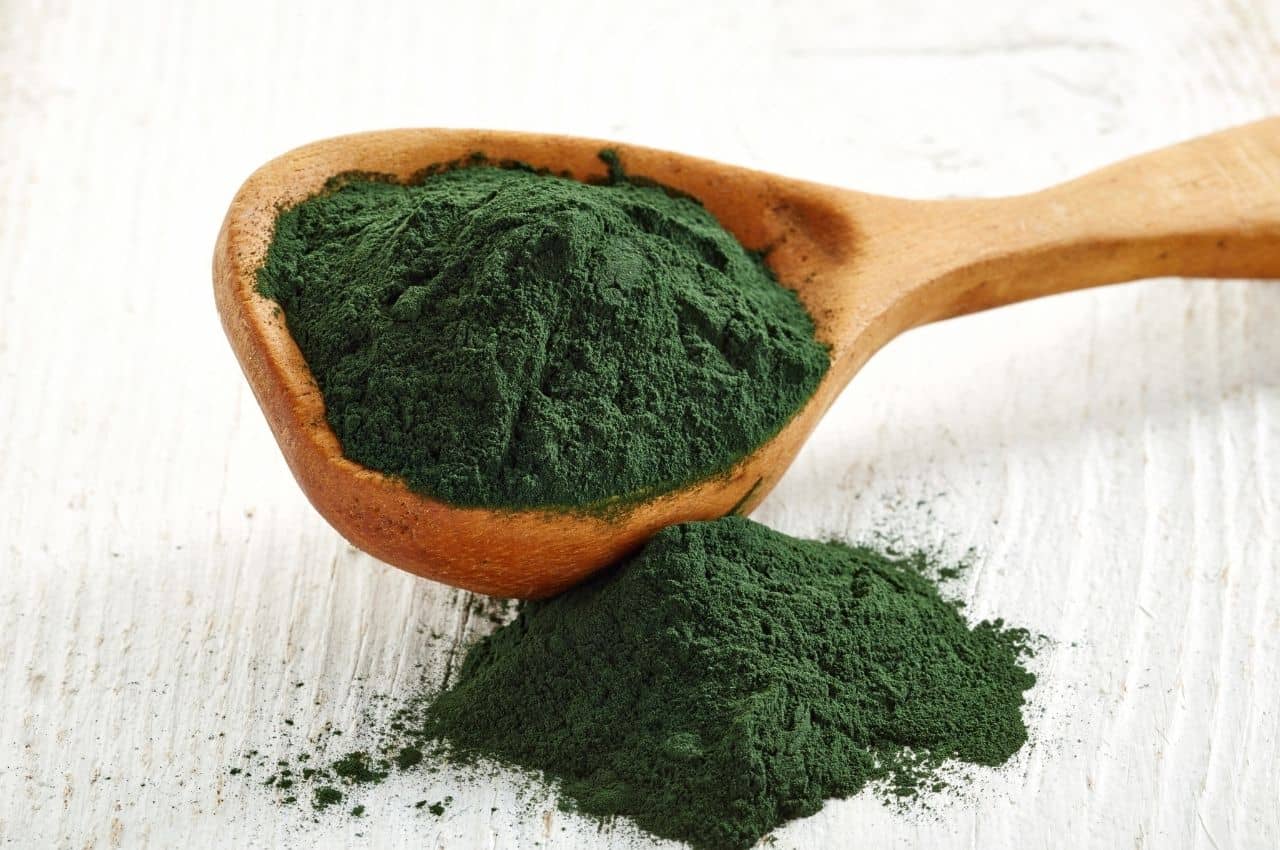

Microalgae
Microalgae such as chlorella and spirulina are packed with health benefits and are also excellent sources of protein (57.5 grams of protein per 100 grams of spirulina). They are rich in essential amino acids, minerals (iron, copper, magnesium, zinc, sodium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, manganese) and vitamin B12. They also contain compounds with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hypolipidemic, and hypoglycemic properties. Spirulina is particularly associated with reducing blood cholesterol and inflammation.
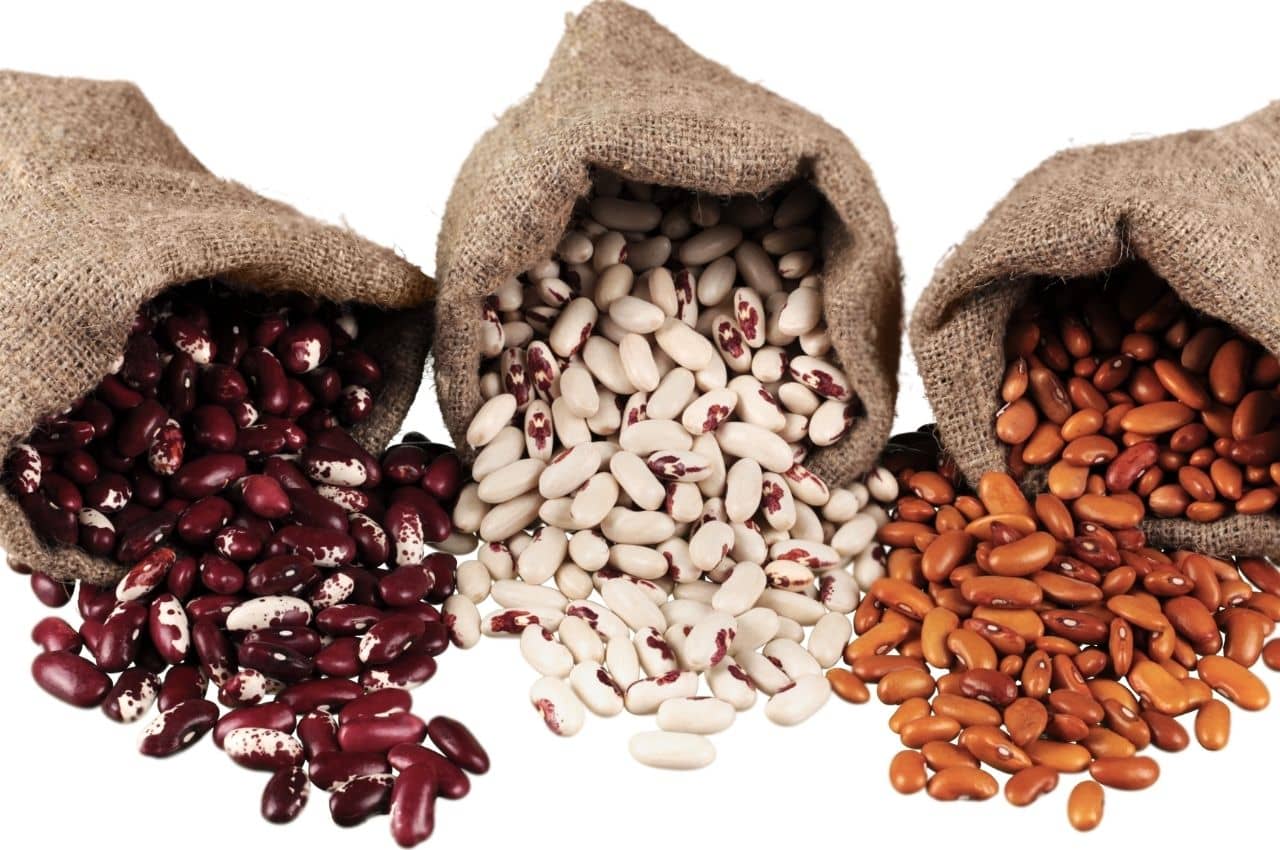

Legumes
Finally, legumes are among the foods rich in protein. Red beans contain 9.63 grams of protein per 100 grams, chickpeas 8.31 grams, lentils about 10 grams, and split peas 8.6 grams per 100 grams. In addition to protein, they are sources of vitamin B and minerals such as iron, calcium, potassium, magnesium, and zinc. They make you feel full, and the iron they contain helps the body transport oxygen. They are low in fat and have a low glycemic index.
Today, there are several alternatives to meat that provide the nutrients the body needs. However, it is important to be mindful of industrial alternatives, which can be high in sodium and other food additives.
Sources:
Proteins. ANSES. Available at: https://www.anses.fr/fr/content/les-prot%C3%A9ines
Iron. ANSES. Available at: https://www.anses.fr/fr/content/le-fer
Ciqual. Food composition table. ANSES. Available at: https://ciqual.anses.fr/
Discover more articles on the microbiota.
What role does sugar play in obesity?
Which foods are richest in vitamin C?
Vitamin C is essential for protecting the body. Regular consumption of fruits and vegetables provides the necessary amount.
Which foods are highest in fiber?
Fiber stimulates digestion, promotes satiety, and lowers cholesterol levels. A varied and balanced diet meets the body's needs.
Take control of your diet with Shido.